Why Mobile Apps Should Prioritize User Experience: A React Native Approach
Why UX matters in Mobile Apps?
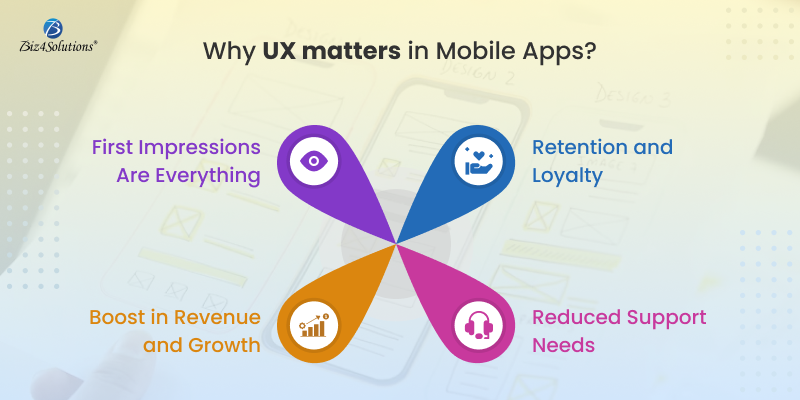
- First Impressions Are Everything: Studies show that users form an opinion about your app within the first few seconds of use. A clean, seamless interface can attract users, while clunky designs or slow response times will likely result in uninstalls.
- Retention and Loyalty: A positive user experience ensures that users keep coming back. With so many apps vying for attention, offering an enjoyable, efficient experience keeps users engaged and builds loyalty.
- Boost in Revenue and Growth: Happy users are more likely to recommend your app, leave positive reviews, and contribute to organic growth. An app that prioritizes UX tends to see higher download rates and better monetization opportunities, such as in-app purchases or subscriptions.
- Reduced Support Needs: Apps that are easy to navigate reduce the need for customer support and troubleshooting, improving overall operational efficiency and lowering costs.
How can React Native change the Game?

Best UX Practices with React Native






