Best Strategies and Practices for Enterprise App Logging!


Application logs play a crucial role in conveying information related to external as well as internal events during the app’s runtime. And most importantly, developers can view this information while it is running. As such, whenever there are occurrences like bugs, security breaches, or anomalies in software deployment, app logs prove handy in analyzing the root cause of the event.
Well-structured logs work wonders in keen observation and prompt action – one can easily and quickly comprehend how the entire system functions and helps to prevent issues well in advance. However, troubleshooting sessions will be productive only if developers adhere to effective logging practices. Improper logging practices will lead to unwanted challenges. Now, the most likely questions that will arise in your mind are:
- What to log?
- What to avoid logging?
- How to log?
Well, this post answers all these questions – the best practices for enterprise app logging and things to avoid while logging.
App Logging Best Practices to Follow
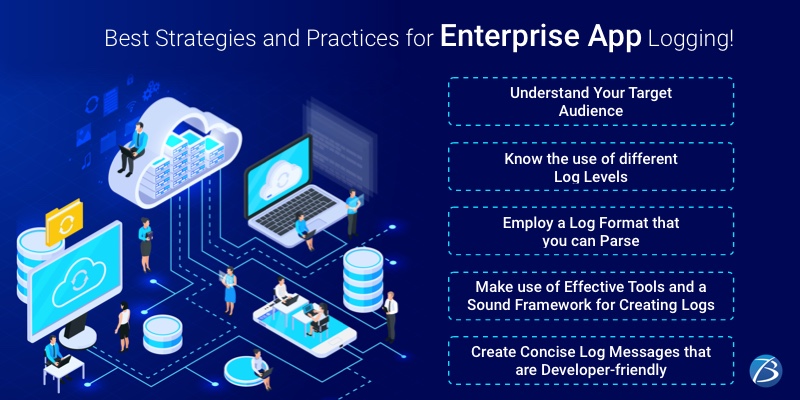
Understand Your Target Audience
While handling logs, it’s important to understand that app logs have two different sets of audiences – machines and humans – and their ways of data handling are quite disparate. If the data is structured, machines can process huge chunks of data automatically and speedily whereas humans fare poorly in processing a substantial amount of data as they need time to read through the logs. But, in the case of unstructured data humans outshine machines.
Therefore, in order to obtain the best results out of your logs, the logs must be created in a way that they are suitable for machines as well as humans – structured for machines, and at the same time, readable for humans.
Know the use of different Log Levels
Log levels indicate the severity of each event within the system and software developers should know when to use each of them. Given below are the commonest log levels available along with their use case scenario.
- Info level deals with the system-specific or user-driven actions like regularly scheduled operations, crucial event banners, and informational messages present in the app behavior.
- Trace level logs enable you to examine the variable values as well as full error stacks. It deals with information such as stack code traces for furnishing information about a particular event. These are to be used for tracking bugs during development.
- Debug level represents specific and comprehensive information. This log assists developers to step through the code and is usually utilized for debugging.
- Error level indicates those error occurrences which may still let the app run continually, but with reduced abilities in the affected paths. So, this level is used for logging error conditions – error events or API calls that return errors.
- Warn level signifies events that are less harmful than errors, but is an indication of red flags that must be investigated. So, use this level to log those events that can potentially become an error – instances when an in-memory cache is nearing capacity or a database call is exceeding the predefined duration. Warn level log will activate automated alerting, and when used while troubleshooting, it will enable you to understand the behavior of the system prior to its failure.
- Fatal level indicates severe error occurrences that may cause the app to abort and result in catastrophic failures. Logging at the fatal level usually indicates the end of the program. Hence, this program is to be used sparingly, only when exiting is the only sensible action to opt for.
Employ a Log Format that you can Parse without much ado
It is not desirable that your observability platform is unable to extract data from your logs. To avoid such a situation, you need to employ a log format that you can parse effortlessly. Also, maintain a consistent log structure so that the data can be easily collected and aggregated.
In the case of several platforms serving a common purpose, standardize a log format for all applications. This will ease out the process of incorporating data into the observability platform even if the teams involved in each application demands visibility into varying attributes. And, if using a customized format, set the log type triggers and create parsing rules as defined by the customer.
Make use of Effective Tools and a Sound Framework for Creating Logs
Leverage the tried and tested logging frameworks and tools instead of reinventing the wheel by creating your own logging environment. This move will not only save your time and hassles. Moreover, a consistent logging framework comes with the following functionalities.
Standard Features of a logging framework
- Setting up various appenders, with each appender having its own custom log pattern and output format
- Adding the logger name & timestamp automatically
- Providing support for several security levels and the option of filtering by these levels
Advanced Features of a logging framework
- Configuring various log-level thresholds for varying code components
- Employing a lossy appender that drops the events at the lower level, whenever queues become full
- Using a logs-summarizing appender that will display via message the number of times a specific message has been repeated; instead of repeating it so many times.
- Placing a threshold at the log level and then configuring this to “also output N lower-level log lines”, whenever the log severity is high.
Create Concise Log Messages that are Developer-friendly
If your log messages carry less information, it will become difficult to capture the necessary information that is needed for creating the context of every crucial event. And, if the log messages are too long, performance issues will crop up. For instance, large log files mean higher I/O and more disk space consumed, and if this aspect is not supported by the file system, the overall performance will get adversely affected. In a nutshell, huge logs consume storage, reduce the speed of search logs, and cause distraction from the core issue, thereby making debugging more difficult.
To address this issue, log messages need to be optimized. For this, you need to gain a rigorous understanding of the functional as well as non-functional expectations of the system, and accordingly plan the quality and amount of messages that you’ll log. In short, you need to strike that perfect balance between the quality and quantity regarding log messages – every log message should be meaningful and relevant to the context. For example, when an app fails to connect and retrieve data from an internal API, logging error messages from either the API or the network state information of the eco-system is more important than including information on the number of apps running or the memory space used by the application.
App Logging Practices to Avoid
Logging Sensitive Data without Proper Encryption
App logs should not expose the following sensitive data:
- PII or Personally Identifiable Information such as username, first/last name, birth date, gender, billing/mailing address, email ID, contact number, credit card number, social security number, etc.
- Business names/contact information such as names of businesses; related persons including staff, clients, etc.; business relations; and business-related transactions with third parties.
- Security credentials, passwords, and auth tokens
- Financial data like card particulars, bank account numbers, and transaction amounts.
Most privacy laws/regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA advise against displaying the aforesaid information through logs as it might lead to security breaches and serious lawsuits. As per the standard protocol, if any financial data is present in the logs, it must be entirely masked or hidden. And, if any business transaction has to be mentioned, one must use a system-generated event ID instead of real business names/identifiers.
How to ensure safety if you need to log some sensitive user data in non-production environments?
- Specify the pieces of information that are to be hidden from the logs – attaching an attribute to every field and mentioning its level of visibility with commands like “show”, “hide”, “mask”, and “encrypt.”
- Write parsers for filtering log messages and for handling the sensitive fields that adhere to the pre-defined instructions as per the related environment.
Vendor lock-in
Your log management should be organized in such a way that you do not get locked to a particular vendor. For this reason, avoid hardcoding vendor libraries; instead, opt for a standard library/wrapper for portability. Using a wrapper would ensure that the code of your app does not explicitly mention the third-party tool, or you can create a logger interface following apt methodologies and include a class that will implement it. Thereafter, add the code that calls the third party to this class.
Logging messages for Troubleshooting only
We all know that troubleshooting is the key purpose of logging. Yet, your log messages should not be meant for troubleshooting only as log messages are immensely helpful in some other tasks as well. So, besides troubleshooting, you can also log messages for the following business tasks:
- Profiling: Logs, being timestamped – at times to the level of milliseconds – can be used as an effective tool for profiling sections of a program. For example, if you log the beginning and end of an operation, you can infer certain performance metrics during troubleshooting without having to add those metrics into the program itself.
- Auditing: Capture notable events, statements describing the activity – sign in, editing, etc. – of the system users.
- Garnering Statistical reports: You can gather interesting stats about a program that is running or the behavior of users. You can also connect it to an alert system for detecting too many errors occurring in a row.
Concluding Words:
Today, logging plays a pivotal role in multiple facets of any enterprise – business intelligence, operations, and marketing strategies. And, following the correct logging techniques and making your logs function effectively is very important. Adhering to the best practices for log monitoring and management will help you to run your business operations smoothly, resolve issues faster, resulting in a speedier development process.
For technical assistance, contact Biz4Solutions, a highly experienced and competent outsourcing software development company in India. We have been offering exceptional services to the global clientele for 10+ years.