How to Choose the Right eLearning Platform for Your Institution?
We are living in an era where digital transformation has revolutionized education, making learning more accessible, engaging, and efficient than ever before. Choosing the right eLearning app development strategy for your institution is critical to staying ahead of the curve, in this rapidly evolving landscape. With countless options available, selecting the best fit requires a strategic approach. This post will walk you through the key factors to consider, helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your institution’s unique goals and learning objectives.
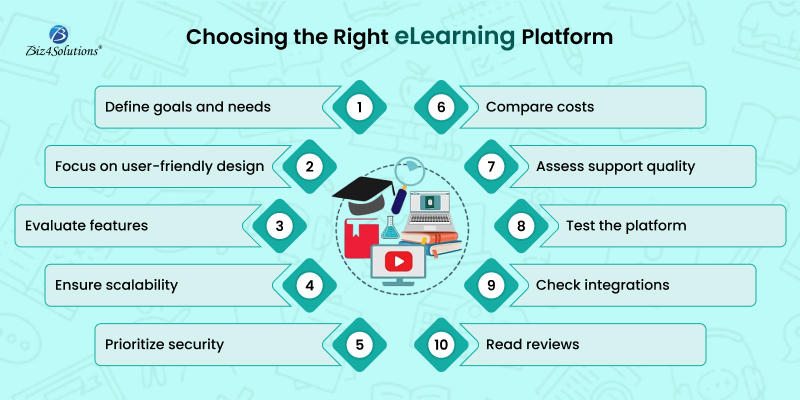
1. Understand Your Goals and Needs
Start by identifying your institution’s goals and needs. Are you looking for a platform to support blended learning, fully online courses, or both? Consider the following:
- The size of your institution
- The age group and learning levels of your students.
- The subjects or courses to be offered.
- The need for scalability and customization.
- Having a clear understanding of these requirements will help narrow down the options.
2. Evaluate User-Friendliness
An eLearning platform must be intuitive and easy to navigate for both instructors and students. Test the platform’s interface to ensure:
- Instructors can quickly create and manage courses.
- Learners can access study materials effortlessly and also track their progress.
- Minimal training is needed to get started.
A complicated platform can lead to frustration and low adoption rates.
3. Assess Features and Functionality
Different platforms offer varying features. When developing the eLearning app, look for ones that align with your teaching methods and institutional goals. Key features to consider include:
- Content creation and management tools.
- Multimedia support (videos, quizzes, and interactive elements).
- Communication tools (forums, chats, and video conferencing).
- Assessment and reporting tools.
- Integration with third-party apps like Google Classroom or Microsoft Teams.
4. Ensure Scalability and Flexibility
Develop software that can grow with your institution. Scalability is essential if you plan to expand your student base or add new courses. Additionally, ensure the eLearning solution is flexible enough to adapt to evolving educational needs, emerging technologies, and demanding end-user preferences.
5. Prioritize Security and Privacy
With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, a secure web or mobile solution is non-negotiable. Verify that the platform complies with data protection regulations, such as GDPR or FERPA, and offers:
- Secure data storage and transmission.
- Role-based access controls.
- Regular updates and maintenance.
6. Review Cost and Licensing
Financial limitations frequently influence decision-making processes. So, compare pricing models, including subscription-based plans, one-time fees, and freemium models. Also, take into consideration, the total ownership expenses including the following:
- Licensing fees.
- Implementation costs.
- Training and support expenses.
7. Check Customer Support and Training
Dependable customer support plays a crucial role. Consider platforms that provide:
- 24/7 support.
- Comprehensive documentation and training resources.
- Community forums or user groups to provide additional assistance.
8. Test the Platform
Before finalizing your decision, ask for a demo or trial period. This firsthand experience enables you to:
- Experience the user interface.
- Assess performance and reliability.
- Gather feedback from instructors and students.
9. Consider Integration and Compatibility
Ensure the platform integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, such as student information systems (SIS) and learning management systems (LMS). Compatibility with various devices and operating systems is also essential to provide a smooth learning experience.
10. Read Reviews and Get Recommendations
Research online reviews and ask for recommendations from other institutions. Hearing about real-world experiences can provide valuable insights into the platform’s strengths and weaknesses.
Final Verdict
Selecting the right eLearning app development strategy is a crucial decision that impacts the quality of education at your institution. By carefully evaluating your goals, budget, and the platform’s features, you can make an informed choice. Remember, the ideal software application or website should not only meet your current needs but also support your organization’s growth and future requirements. Take your time, involve stakeholders, pair up with seasoned software development professionals, and choose wisely for a successful eLearning journey.