Top Challenges in Explainable AI and Ways to Address Them

In my previous post,“What is Explainable AI and How is it Different from Generative AI?”, I explored what makes Explainable AI (XAI) such an essential part of today’s AI ecosystem and how it differs from the fast-evolving world of Generative AI. That post set the stage for understanding why transparency in AI systems is becoming so critical.
Now, let’s take the conversation a step further. While the idea of XAI sounds promising, implementing it in real-world systems comes with its own set of challenges—from accuracy vs. interpretability trade-offs to regulatory and privacy concerns, several hurdles stand in the way. In this post, we’ll dive into the key obstacles organizations face with XAI and explore practical measures to overcome them.
Accuracy vs. Interpretability: Striking the Right Balance
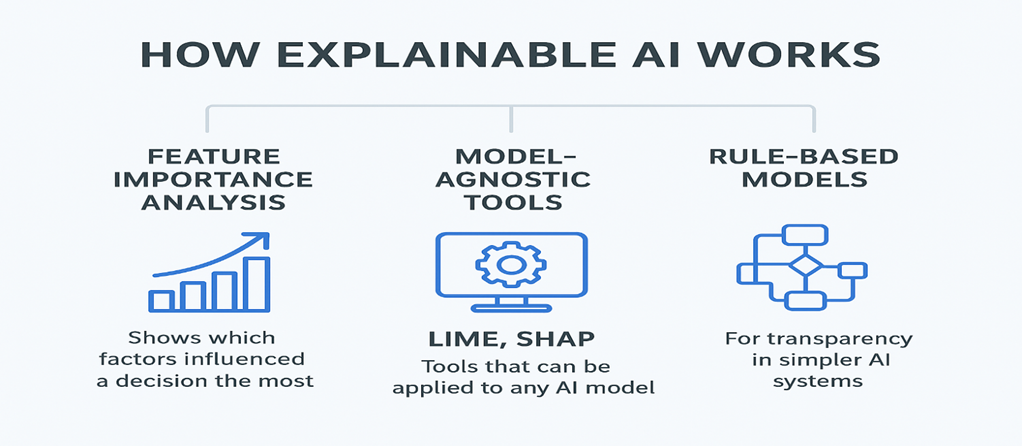
One of the biggest dilemmas in XAI is choosing between accuracy and interpretability. High-performing models like deep neural networks are often black boxes—extremely accurate but hard to explain. Simpler models like decision trees are easy to interpret but might fall short when solving complex problems.
Possible Solutions:
Hybrid Approaches: Use a mix of interpretable models with black-box models where explainability is critical.
XAI Tools: Leverage solutions like LIME or SHAP that explain complex model predictions without sacrificing too much accuracy.
No Standard Definitions or Metrics
“Explainability” doesn’t mean the same thing to everyone. Some view it as model transparency, others as end-user understanding. This lack of consensus makes it tough to set industry-wide benchmarks.
Possible Solutions:
Unified Standards: Collaborate with regulators and AI bodies to define common frameworks for explainability.
Industry-Specific Metrics: Customize evaluation methods for sectors like healthcare, finance, or transportation based on risk and compliance needs.
Post-hoc Explanations vs. Built-in Interpretability
Many current tools try to explain decisions after the model is built (post-hoc). Critics argue that these explanations can be approximations, not true reflections of how the model works internally.
Possible Solutions:
Transparent by Design: Encourage research into models that are inherently interpretable rather than relying only on after-the-fact explanations.
Policy Support: For sensitive areas like healthcare or autonomous driving, regulations could mandate interpretable models.
One Explanation Doesn’t Fit All
Different people need different levels of insight. Data scientists want in-depth technical details. End-users prefer simple, easy-to-digest explanations. Regulators focus on compliance and accountability.
Possible Solutions:
Layered Explanation Systems: Offer technical details for experts while giving summarized, user-friendly insights to non-technical audiences.
Interactive Dashboards: Let stakeholders drill down into explanations at their preferred depth.
Balancing Transparency with Privacy and Security
Making models too transparent can reveal sensitive data or make systems vulnerable to attacks if bad actors learn too much about how decisions are made.
Possible Solutions:
Privacy-Preserving XAI: Use technologies like differential privacy or federated learning to protect data while offering explainability.
Access Controls: Share sensitive explanations only with authorized stakeholders.
Regulatory and Ethical Hurdles
Regulations such as the EU AI Act and GDPR’s Right to Explanation push organizations toward explainable AI, but the rules are sometimes vague, creating compliance headaches.
Possible Solutions:
Proactive Compliance Planning: Engage legal and compliance experts early in the AI development cycle.
Ethics-First Approach: Integrate fairness, accountability, and transparency principles right from the start.
Technical Limitations of Current XAI Tools
Tools like LIME and SHAP are powerful but often slow, resource-heavy, and inconsistent across models.
Possible Solutions:
More Research Funding: Support the development of faster, scalable, and more reliable XAI methods.
Cloud-Based Platforms: Make advanced XAI tools more accessible through AI-as-a-Service offerings.
Points to Ponder
Explainable AI sits at the crossroads of technology, ethics, and regulation. The challenges range from technical complexity to privacy and compliance concerns. However, by embracing hybrid modeling, standardized metrics, privacy-preserving techniques, and user-specific explanations, organizations can make significant progress toward building AI systems that are not only powerful but also transparent and trustworthy. As AI adoption accelerates, achieving the right balance between accuracy, transparency, and trust will shape the future of responsible AI.