Developing Scalable EdTech Platforms for Global Classrooms: Expert Tips
The concept of virtual classrooms has gained momentum in recent years. The integration of innovative technologies in education platforms has opened up new avenues of learning and collaboration, enabling students and educators to connect across geographical boundaries. Today, global classrooms have become very popular where students from every corner of the globe can access learning content online. A global platform connects students, educators, and institutions while accommodating different languages, cultures, time zones, and learning preferences. This post will guide you through the key considerations of developing scalable EdTech platforms that cater to the diverse needs of global classrooms, ensuring accessibility, inclusivity, and UX.
Why do EdTech Platforms need to be Scalable?
As classrooms move online, the ability to scale becomes crucial to providing uninterrupted access to learning resources, tools, and experiences. A scalable platform is one that can grow and adapt to changing user demands, whether it’s increasing the number of students, adding new features, or expanding to different regions. Scalable platforms can easily integrate multiple languages and support localized content while offering personalized learning experiences. A scalable infrastructure ensures the platform can handle surges in traffic, especially during peak times such as exam periods, school registrations, or the release of new courses. The education sector is ever-evolving, and a scalable platform allows the integration of new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and gamification, ensuring the platform stays ahead of the curve. In a nutshell, the user base of an EdTech platform can grow exponentially over time if it’s scalable.
Key Features of a Scalable EdTech Platform
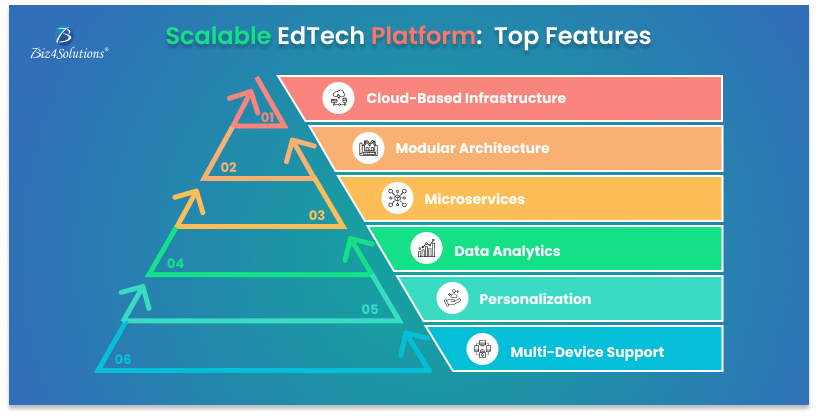
Cloud-Based Infrastructure
The cloud is the backbone of scalability. Cloud hosting providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure allow EdTech platforms to scale up or down as needed. Cloud infrastructure supports data storage, security, and fast content delivery, ensuring that learners can access content anytime, anywhere.
Modular Architecture
A modular approach makes way for effortless expansions and upgrades. Features such as user authentication, content management, payment processing, and analytics should be developed in a way that allows them to function independently and be updated without affecting the entire system.
Microservices
By using microservices, EdTech platforms can break down complex apps into smaller, manageable services. Each service can operate independently, scale as required, and be updated without disrupting the rest of the platform. This promotes flexibility and reduces downtime during upgrades.
Data Analytics and Reporting
Data plays a key role in understanding student performance and optimizing learning experiences. A scalable platform should be able to process large amounts of data in real time, providing actionable insights for educators and administrators.
Personalization
Every student learns differently. Scalable EdTech platforms should offer personalized learning paths, adaptive assessments, and AI-driven recommendations to keep students engaged and help them progress at their own pace.
Multi-Device Support
With students accessing content on laptops, tablets, and smartphones, it’s important to ensure your platform is responsive and provides a seamless UX across all devices. This flexibility allows learners to access their courses and materials from any device, any location.
Technological Tools and Approaches for Global Classrooms
1. Video Conferencing and Collaboration
Tools like Slack, WhatsApp, Google Meet, Zoom, Cisco Webex, WeChat, Microsoft Teams, etc. facilitate live virtual classes, discussions, and webinars; enabling real-time communication between learners and educators across different parts of the globe. Platforms like Padlet, Jamboard, Google Workspace (Docs, Sheets, Slides), Microsoft 365, Miro, etc. foster real-time collaboration on projects, assignments, and brainstorming; facilitating teamwork and global peer-to-peer interaction. Online Project Management tools such as Trello, Asana, and Basecamp help students and teachers organize tasks, track deadlines, and manage projects. This way, global teams stay coordinated despite different time zones.
2. Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things
AI Tools like ChatGPT, Grammarly, Edmentum, DreamBox, etc. support personalized learning through adaptive content and also provide feedback on writing and assignments. This enables the customization of learning paths based on a learner’s pace, strengths, and weaknesses. IoT and Smart Classroom Devices like Interactive projectors, and Smart tablets support features like automated attendance and smart monitoring to create a tech-driven learning environment.
3. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
VR and AR enhance end-user engagement by bringing subjects to life, such as virtual field trips or interactive science experiments. Some examples include Google Expeditions, Nearpod VR, and Merge EDU which provide immersive learning experiences, enabling learners to explore historical sites, cultural landmarks, or scientific phenomena.
4. LMS
Learning Management Systems like Moodle, Blackboard, Google Classroom, and Canvas centralize course content, assignments, assessments, and grading and also support asynchronous learning for flexibility in global time zones. One can organize course materials, track progress, and communicate effectively using an LMS.
5. Game Elements and Remote Assessment
Integrating game elements into lessons makes learning all the more engaging and interactive. Digital Assessment Tools such as Kahoot!, Poll Everywhere, Mentimeter, Quizizz, etc. provide instant feedback through quizzes, polls, and interactive games. Using technologies like ProctorU and Examity; students can be monitored during online assessments to prevent academic dishonesty.
6. Digital Content Creation and Interactive Whiteboards
Platforms like Canva, Adobe Spark, Prezi, Powtoon, etc. enable students and teachers to create visually appealing presentations and projects and promote creativity and storytelling skills. Interactive Whiteboards such as Jamboard, SMART Board, Promethean, etc. support interactive lessons and brainstorming sessions; engaging students with visual and hands-on activities.
7. Cloud Storage and Sharing Platforms
Google Drive, Dropbox, and OneDrive allow students and educators to store and share resources securely; facilitating collaboration on shared documents and projects.
8.Language Translation
Tools like Duolingo, Google Translate, Memrise, Rosetta Stone, or AI-based real-time translators break language barriers in multicultural global classrooms.
9. Open Educational Resources (OERs)
Coursera, YouTube Education, Khan Academy, EdX, etc. provide free or affordable access to high-quality educational content and promote self-paced and inclusive learning.
10. Social Media for Learning
LinkedIn Learning, YouTube, Facebook Groups, and Twitter, facilitate discussions, resource sharing, and connecting with subject matter experts, making way for global networking among students and educators.
Top Considerations for Developing Scalable EdTech Solutions
Prioritize UX: User experience is the key to engagement. A simple, intuitive, and user-friendly interface ensures that learners and educators can easily navigate the platform. Continuous feedback from users will help you identify pain points and areas for improvement.
Ensure Robust Security: With vast amounts of personal and academic data being exchanged, security is paramount. Implement end-to-end encryption, strong user authentication, and regular security audits to protect user data and maintain privacy.
Invest in Performance Optimization: Speed and performance are critical to keeping users engaged. Invest in content delivery networks (CDNs) to reduce latency and ensure that learners can access resources quickly and reliably, no matter where they are in the world.
Integrate Third-Party Tools: To enhance functionality, integrate with third-party tools such as video conferencing, collaborative document editing, and plagiarism detection systems. These tools help improve the overall learning experience and can scale as needed.
Plan for Globalization: Ensure that your platform is designed to handle multiple languages, currencies, and time zones. This may involve incorporating translation features, culturally relevant content, and flexible payment systems.
Adopt Agile Development: An agile development approach ensures that your EdTech platform can quickly adapt to changing requirements. Regular testing and updates will help you address bugs, introduce new features, and maintain a competitive edge.
Challenges in Scaling EdTech Platforms
While scalability is essential, it comes with its own set of challenges:
- Cost of Infrastructure: As you scale, the cost of infrastructure and cloud services can increase. It’s essential to strike a balance between scalability and cost-effectiveness.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Global platforms must adhere to various data privacy laws such as GDPR, FERPA, and CCPA. Navigating these regulations can be complex but is necessary to build trust and comply with local laws.
- User Adoption: As platforms expand, maintaining high user engagement can be challenging. Ongoing user education, customer support, and community building are essential for keeping learners motivated.
Final Words
Developing a scalable EdTech platform is an investment in the future of education. However, it requires careful planning and strategic software development. Success lies in selecting the right resources and cutting-edge technologies that best suit your use case. Are you ready to scale your EdTech platform to serve a global classroom? Start by focusing on the right infrastructure, user experience, and continuous innovation, and you’ll be well on your way to transforming education for the future.