The Role of Quantum Computing in the Future of Banking App Development
The banking industry, a cornerstone of the global economy, has always embraced innovation to improve efficiency, security, and customer satisfaction. As we look toward the future, one technology poised to revolutionize fintech and banking software development is quantum computing. With its ability to perform complex calculations at unprecedented speeds, quantum computing has the potential to reshape how we approach banking systems, data security, and customer experiences.
Understanding Quantum Computing
Quantum computing uses the principles of quantum mechanics for processing information. Unlike classical computers, which use binary bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, that can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to superposition. This unique property allows quantum computers to solve problems that are practically unsolvable for classical machines, especially in areas like cryptography, optimization, and large-scale data analysis.
How to apply Quantum Computing in Banking App Development
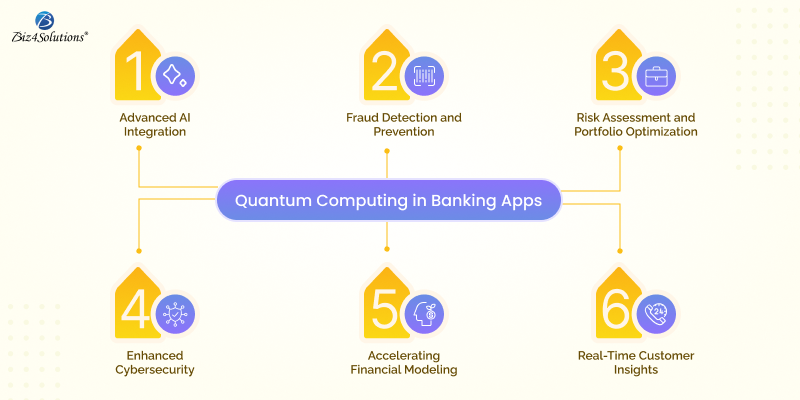
1. Fraud Detection and Prevention
Fraudulent activities in banking are becoming increasingly sophisticated, and traditional systems often struggle to detect subtle patterns in vast datasets. Banking apps handle millions of transactions daily, making fraud detection a top priority. Quantum computing’s ability to process and analyze massive amounts of data in real time could significantly improve fraud detection mechanisms. By rapidly identifying patterns and anomalies, quantum-powered algorithms can flag suspicious transactions more accurately, reducing false positives and minimizing losses.
2. Risk Assessment and Portfolio Optimization
Risk management is a cornerstone of banking, involving complex calculations to assess financial risks and optimize investment portfolios. Classical algorithms often struggle with the complexity of calculating the optimal asset mix under uncertain market conditions. Quantum computers excel in solving optimization problems by evaluating countless variables and scenarios simultaneously. This capability can help banks create more robust risk assessment models and develop optimal investment strategies for their clients. For asset management and trading apps as well, quantum computing offers a game-changing advantage in portfolio optimization and risk assessment.
3. Enhanced Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a critical concern for banking and finance apps. As quantum computing advances, so does the threat to current encryption methods, such as RSA and ECC, which rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers—a task quantum computers can solve exponentially faster. The solution: quantum cryptography that uses the principles of quantum mechanics to secure communication and protect data from eavesdropping. Unlike classical encryption, which relies on complex mathematical algorithms, quantum cryptography leverages the properties of quantum particles for secure key distribution. Techniques like quantum key distribution (QKD) can provide virtually unbreakable encryption, ensuring secure communication and data protection in an era of advanced cyber threats. Such mechanisms help financial institutions safeguard customer data against threats posed by quantum-enabled cyberattacks.
4. Accelerating Financial Modeling
Banks rely heavily on financial models to make strategic decisions, predict market trends, and manage assets. Traditional computing systems can be slow when simulating complex models. Quantum computing can accelerate this process, enabling banks to make faster, more accurate decisions in volatile markets.
5. Real-Time Customer Insights
Modern banking apps thrive on delivering personalized experiences. Quantum computing can process vast amounts of customer data in real time, providing actionable insights into spending patterns, financial goals, and user preferences. These insights can drive the development of features like customized financial advice, targeted marketing, and dynamic credit scoring and the outcome is an enhanced customer experience.
6. Advanced AI Integration
Quantum computing enhances artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning models by accelerating training processes and improving accuracy. Banking apps powered by quantum-enhanced AI can provide smarter chatbots, predictive analytics, and better financial forecasting, transforming how users interact with their financial services.
Challenges in Adopting Quantum Computing
While the potential is immense, the road to widespread quantum computing adoption is not without challenges:
- Invest in Research and Development: Collaborations with seasoned tech companies and quantum startups can accelerate the exploration of quantum applications.
- Develop Quantum-Resistant Algorithms: Preparing for the post-quantum cryptographic era will ensure long-term security.
- Educate and Train Teams: Building expertise in quantum computing within banking app development teams is crucial.
- Adopt a Hybrid Approach: Integrating classical and quantum systems can provide incremental benefits while addressing current limitations.
Key Takeaways
Quantum computing represents a transformative force in the evolution of banking app development. By enabling unparalleled computational power, it promises breakthroughs in security, data analysis, and customer experience. Although challenges remain, the forward-thinking adoption of quantum technologies will position banks at the forefront of innovation, delivering smarter, safer, and more efficient apps for their customers. The future of banking lies in the quantum realm—are you ready to make the leap?