 In today’s SaaS landscape, feature sets alone are no longer enough to define a product’s success. Speed, adaptability, and intelligent automation increasingly define whether a platform scales smoothly or collapses under operational complexity. As entrepreneurs, CTOs, and CEOs plan custom SaaS and AI-driven software, one architectural shift is gaining serious momentum: multi-agent systems. These systems are quietly changing how SaaS workflows are designed, executed, and optimized; and they are especially relevant for companies building next-generation AI-powered platforms.
In today’s SaaS landscape, feature sets alone are no longer enough to define a product’s success. Speed, adaptability, and intelligent automation increasingly define whether a platform scales smoothly or collapses under operational complexity. As entrepreneurs, CTOs, and CEOs plan custom SaaS and AI-driven software, one architectural shift is gaining serious momentum: multi-agent systems. These systems are quietly changing how SaaS workflows are designed, executed, and optimized; and they are especially relevant for companies building next-generation AI-powered platforms.Why Are Traditional SaaS Workflows Starting to Break?
What Are Multi-Agent Systems in the Context of SaaS?
A multi-agent system is a coordinated network of autonomous AI agents, each responsible for a specific role, working collaboratively toward shared goals. Instead of one monolithic AI handling everything, tasks are decomposed and distributed across specialized agents that communicate, validate outcomes, and adapt based on context.
In SaaS software development, this approach aligns naturally with modular architectures. One agent can interpret user intent, another can retrieve or analyze data, a third can execute actions across backend services, and a supervisory agent can orchestrate the entire workflow. The outcome goes beyond basic automation and moves into coordinated, intelligent execution.
An industry research study by Gartner supports this shift. It predicts that task-specific AI agents will be implemented in 40% of enterprise apps by 2026. This highlights how rapidly agent-based architectures are becoming mainstream in production software. 

How Multi-Agent Systems Are Changing SaaS Workflows
The most immediate impact of multi-agent systems is seen in workflow orchestration. Instead of static, step-by-step automation, workflows become adaptive. Agents operate in parallel, share context, and make local decisions while aligning with a global objective. This dramatically improves responsiveness in SaaS products handling real-time data, high user concurrency, or complex business logic.
Another major shift is parallel execution. Multi-agent architectures allow tasks to be processed simultaneously rather than sequentially. For SaaS platforms offering analytics, AI copilots, or operational automation, this leads to faster turnaround times and better user experiences without linear scaling of infrastructure costs.
Most importantly, multi-agent systems introduce context-aware decision-making into workflows. Agents don’t just execute commands; they evaluate confidence, detect ambiguity, and escalate to humans only when necessary. This creates a balance between autonomy and control—something many SaaS founders struggle to achieve with traditional automation. 

Case Study Spotlight: Applying Multi-Agent Systems in a Real SaaS Product
The relevance of multi-agent systems becomes clearer when viewed through a real implementation. A strong example is MultiTaskerAI, a custom AI-powered SaaS solution built using a multi-agent architecture to automate everyday operational and knowledge-work tasks.
In this system, a central supervisory agent evaluates user intent and dynamically assigns tasks to specialized agents. These agents are responsible for functions such as research, content generation, scheduling, communication, and validation. Instead of operating in isolation, agents collaborate, exchange intermediate results, and refine outputs collectively.
A critical design element in MultiTaskerAI is its confidence-driven workflow. When an agent’s confidence falls below a defined threshold, the system intelligently escalates the task rather than producing unreliable output. This ensures accuracy while still minimizing manual effort; an essential requirement for enterprise-grade SaaS platforms.
This case study demonstrates how multi-agent systems can power scalable task automation, reduce operational friction, and deliver adaptive workflows that evolve with user needs. It also reflects how AI, SaaS architecture, and intelligent automation converge in real-world custom software development.
What Problems Does This Solve for SaaS Founders and CTOs?
For leaders planning custom SaaS or AI-driven platforms, multi-agent systems directly address some of the most persistent challenges. They reduce dependency on rigid workflow logic, making platforms easier to extend and maintain. They support scalability by distributing intelligence rather than centralizing it. They also enable smarter automation that improves user experience without sacrificing reliability.
A question worth asking at this stage is: Is your SaaS workflow designed to adapt as your product, users, and data grow; or will it require constant re-engineering? Multi-agent architectures are increasingly becoming the answer for teams seeking long-term flexibility. 

Why Multi-Agent Systems Matter for Custom SaaS Development
From a software development perspective, multi-agent systems fit naturally into modern cloud-native, microservices-based SaaS platforms. They complement AI models, APIs, and backend services rather than replacing them. When designed correctly, they enhance observability, resilience, and decision quality across the application.
For businesses investing in custom SaaS development, this approach unlocks faster innovation cycles, better automation ROI, and a foundation that can evolve as AI capabilities mature. It also creates differentiation in competitive markets where intelligent workflows increasingly define product value. 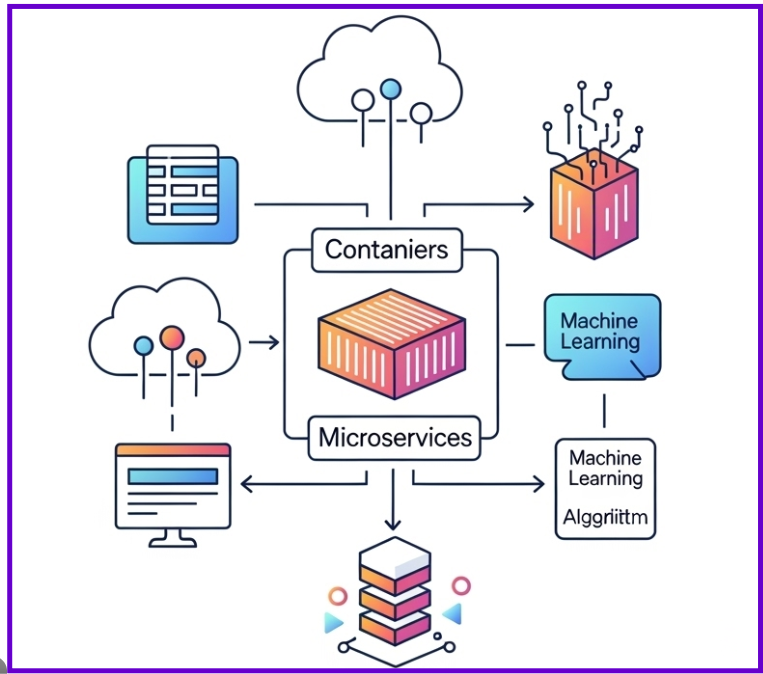

Final Thoughts
Multi-agent systems are not a theoretical concept anymore; they are actively reshaping how SaaS workflows are built and executed. By enabling autonomous collaboration between specialized AI agents, they move SaaS platforms beyond basic automation toward intelligent, adaptive orchestration.
For entrepreneurs, CTOs, and CEOs planning custom SaaS or AI-powered software, the key question is no longer whether to use AI, but how intelligently it is embedded into workflows. Multi-agent systems offer a proven, scalable path forward; especially when implemented by experienced software development teams that understand both AI architecture and real business workflows.
